Table of Contents
Toggle1. The Rise of Electric Vehicles: A Global Shift
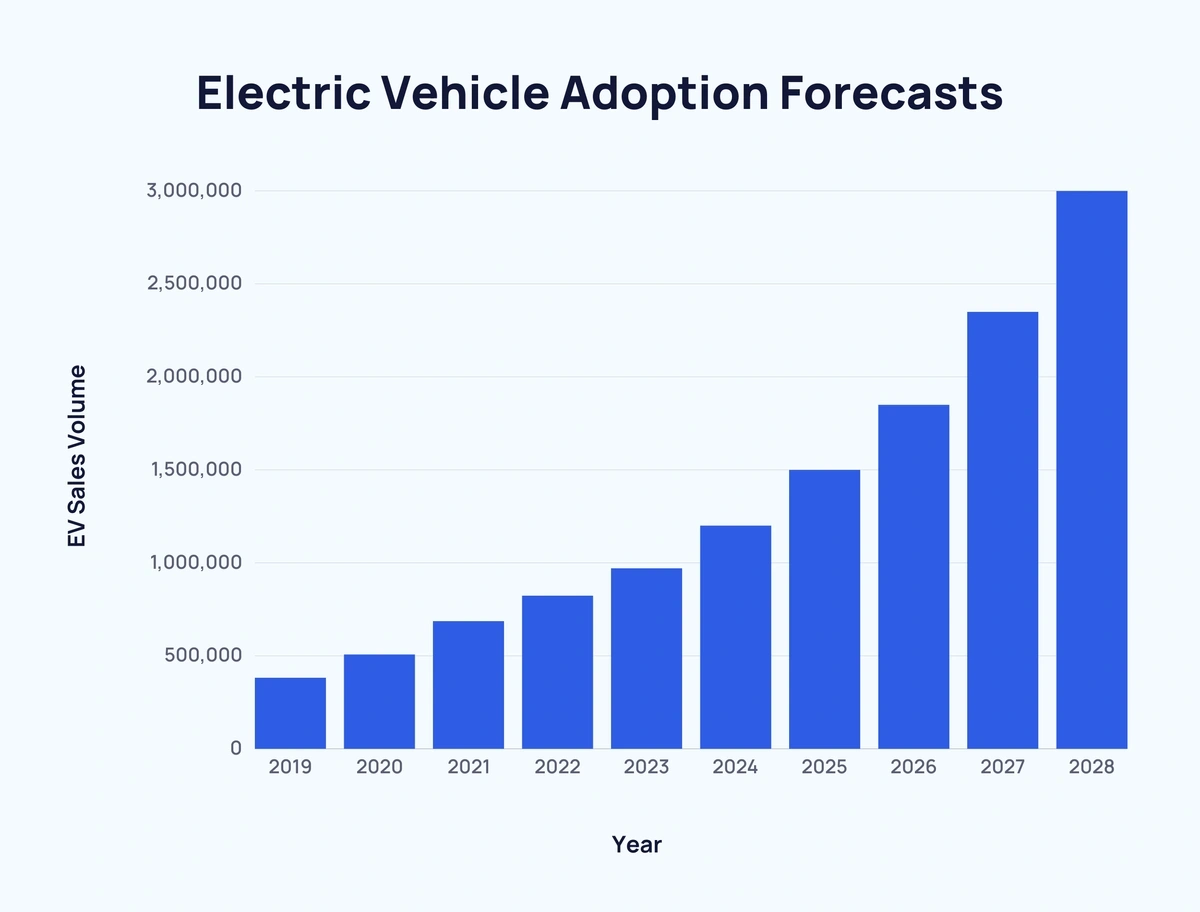
Electric vehicle adoption is no longer a niche trend but a global movement that is reshaping the automotive industry. According to recent reports, the market for electric vehicles is projected to grow exponentially in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and changing consumer preferences. Governments and automakers alike are prioritizing the transition to electric mobility, setting ambitious targets for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the promotion of clean energy solutions.
Several key factors are contributing to the widespread adoption of EVs:
- Environmental Awareness: Consumers and governments are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. EVs offer a cleaner alternative that produces zero tailpipe emissions and reduces the overall carbon footprint.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in battery technology have made EVs more affordable, efficient, and capable of longer driving ranges. Advancements in charging infrastructure are also making EVs more convenient to own and operate.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Many governments around the world are offering financial incentives, such as tax rebates, purchase subsidies, and reduced registration fees, to encourage EV adoption. Additionally, stricter emissions regulations are pushing automakers to transition away from fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
2. Key Benefits of Electric Vehicle Adoption
The transition to electric vehicles comes with numerous benefits for consumers, industries, and the environment.
- Environmental Impact: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, which means they help reduce air pollution and greenhouse gases. This is particularly important in urban areas, where vehicle emissions contribute significantly to poor air quality and climate change.
- Lower Operating Costs: Electric vehicles are generally more affordable to operate than traditional vehicles. EVs have fewer moving parts, which leads to lower maintenance costs. Additionally, electricity is often cheaper than gasoline, making the cost per mile for EVs lower than that of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are significantly more efficient than gasoline engines. EVs convert a higher percentage of the energy from the battery into motion, leading to less wasted energy.
- Quiet and Smooth Driving Experience: EVs are known for their quiet operation and smooth acceleration. The absence of an internal combustion engine means that EVs produce less noise, resulting in a quieter and more enjoyable driving experience.
3. Challenges Facing Electric Vehicle Adoption
Despite the promising outlook, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles faces several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure the success of the transition:
-
Charging Infrastructure: One of the main barriers to EV adoption is the lack of widespread and easily accessible charging infrastructure. Although the number of public charging stations is growing, they are still not as widespread or convenient as gas stations, especially in rural or underserved areas. Fast-charging options and home charging solutions are critical to overcoming this barrier.
-
Battery Technology and Range Anxiety: Although EV battery technology has made significant strides, battery performance and range remain a concern for many consumers. Range anxiety—the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station—can discourage potential EV buyers, particularly for long-distance travel. While many EVs now offer ranges sufficient for daily driving, range anxiety remains a barrier for widespread adoption.
-
Upfront Cost: While EVs tend to be more affordable in the long run due to lower operating costs, their upfront cost is still higher than that of traditional vehicles. Although prices are gradually falling, many consumers are deterred by the initial price tag of electric vehicles, despite available incentives.
-
Supply Chain and Resource Availability: The production of EV batteries relies heavily on critical raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The demand for these materials is increasing rapidly as EV adoption rises, raising concerns about the sustainability of mining practices, the availability of resources, and the potential environmental impacts of resource extraction.
4. Technological Innovations and Industry Trends
As www.truthin24.com continues to gain momentum, several technological innovations and industry trends are helping to shape the future of electric mobility.
-
Battery Advancements: One of the most significant advancements in the EV space is the continued development of battery technology. Manufacturers are working to improve battery efficiency, reduce costs, and increase energy density. Solid-state batteries, which promise faster charging times and greater energy capacity, are particularly exciting and may play a key role in the future of EVs.
-
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: Vehicle-to-grid technology allows electric vehicles to not only draw power from the grid but also feed energy back into it. This bidirectional flow of electricity could help stabilize the grid, store renewable energy, and even provide backup power for homes or businesses.
-
Autonomous Electric Vehicles: The convergence of electric vehicle technology and autonomous driving is another exciting trend. Autonomous electric vehicles (AEVs) could revolutionize transportation by reducing traffic accidents, improving traffic flow, and offering more sustainable, shared mobility options.
-
Wireless EV Charging: Another innovative development is wireless or inductive charging, which allows vehicles to charge without needing to plug into a charging station. This technology could eliminate the need for physical charging cables, making the charging process more convenient and seamless for EV owners.
5. The Role of Governments in Promoting EV Adoption
Governments around the world are crucial to the success of electric vehicle adoption. Many countries have set ambitious goals to phase out internal combustion engine vehicles and promote cleaner alternatives, such as electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
-
Incentives and Subsidies: Governments are offering a wide range of incentives to encourage consumers to purchase electric vehicles, including tax credits, rebates, and exemptions from tolls or parking fees. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of EVs and make them more affordable to a wider range of consumers.
-
Emissions Regulations and Bans on ICE Vehicles: Several countries and cities are introducing stricter emissions regulations and setting timelines to ban the sale of new gasoline and diesel vehicles. For example, the European Union aims to reduce carbon emissions and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, with a push to have all new cars sold be zero-emission by 2035.
-
Investment in Charging Infrastructure: Governments are also investing in the expansion of charging networks. Public-private partnerships and collaborations between automakers, energy providers, and government entities are helping build a more robust and widespread charging infrastructure to support the growing number of EVs on the road.
6. Consumer Education and Awareness
While adoption rates are growing, consumer education remains key to accelerating the transition to electric mobility. Many consumers are still unfamiliar with EV technology or have misconceptions about their performance, costs, and benefits. Dealerships, automakers, and governments must invest in educating consumers about the advantages of EVs and address concerns such as range anxiety, charging times, and total cost of ownership.
Conclusion: The Future of Electric Vehicle Adoption
Electric vehicle adoption is on an upward trajectory, driven by technological advancements, government support, and growing environmental awareness. While challenges such as charging infrastructure, battery technology, and cost remain, the future looks promising for the widespread adoption of EVs. As automakers continue to innovate, and governments invest in cleaner infrastructure, the transition to electric mobility will play a crucial role in reducing global emissions and fostering a more sustainable transportation system.
By embracing electric vehicles, consumers can enjoy the benefits of lower operating costs, quieter and smoother driving, and a reduced environmental footprint. With continued innovation and supportive policies, electric vehicles will undoubtedly be a cornerstone of a sustainable and greener future for transportation.